What is GeoServer?
GeoServer is a Java-developed tool that allows editing and visualization of geographic data. It uses standards established by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), enabling the development of web mapping solutions by integrating various geographic data repositories with simplicity and high performance. GeoServer is a fully functional Web Map Service (WMS), Web Coverage Service (WCS), and Web Feature Service (WFS) server that follows the specifications of the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC).
The focus of GeoServer is to facilitate the use and support of open standards, allowing anyone to quickly share their geospatial information in an interoperable way. Here, I will leave two references to the GeoServer documentation and the Open Geospatial Consortium.
Now let’s explore each service and its main functionalities:
Web Map Service (WMS)
Provides an HTTP interface for requesting georeferenced map images from one or more geospatial databases. A WMS request defines a geographical layer and an area of interest to be processed, with the response being one or more map records in an image format (JPEG, PNG, etc).
Web Coverage Service (WCS)
Designed to simplify remote access to coverages, such as raster format images. Unlike the WMS standard that returns static maps rendered as images, WCS provides data with its original description and semantics for interpretation.
Web Feature Service (WFS)
Returns vector data, encoding and transferring information in Geography Markup Language (GML), a subset of XML. Users have access to these spatial data and can create, update, and delete.
Web Processing Service (WPS)
Allows the publication of geospatial processes and remote execution of these processes through web service calls. These processes can perform tasks such as spatial data analysis, geospatial data transformation, and information generation from geospatial data. To enable this service in GeoServer, an extension is required.
System Architecture Design
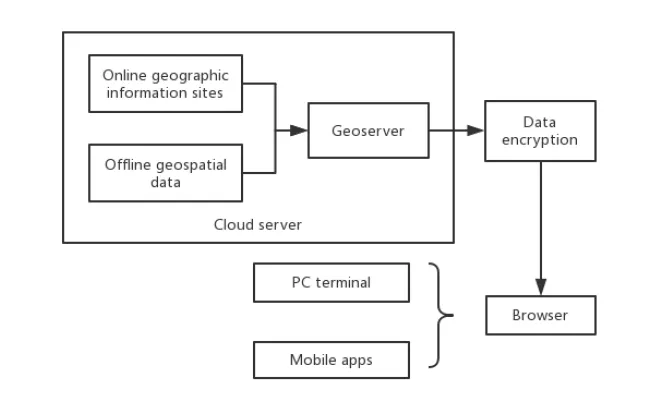
In the article ‘Construction and Application of Field Investigation Support Platform for Land Spatial Planning Based on GeoServer’ by Yao Dai et al., an example of a system architecture using GeoServer is presented. This system processes geographic data for classification and publication on a cloud server, with data encrypted for security before being made available via WebGIS.
Why Use or Not Use GeoServer?
Advantages:
- Supports open standards like WMS, WFS, WCS, WPS, facilitating integration with other GIS systems and applications.
- It can connect to a variety of spatial data sources, including PostGIS databases, shapefiles, GeoTIFF, and others.
- Open-source and continuously improved by an active community, meaning no licensing costs.
- Relatively simple user interface for managing layers and styles.
- Works well with other open-source tools such as QGIS, OpenLayers, Leaflet, Python, etc.
Disadvantages:
- May face performance and scalability challenges with large data volumes or high request rates.
- It could be complex for new GIS users or those with limited technical experience.
- Requires regular maintenance and updates, like any software, to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Advanced functionalities may require in-depth technical knowledge or programming skills.

